In this tutorial, we will be explaining the steps to install Next Cloud on Ubuntu 16.04 server.
As you are here to read the next cloud installation tutorial, you might be knowing about Next Cloud and it’s usage. NextCloud is a free and open source file sharing platform that can be installed on a private server. NextCloud eliminates the need of using a third party cloud hosting platform for storing and using the information such as files, calendars, contacts etc.
Being a fork of OwnCloud, the main difference of NextCloud from OwnCloud is that the software is completely open source. We will be going through the installation and configuration procedure without taking much time to explain the features of next cloud. To know more about nextcloud, just check out the official next cloud website
Prerequisites
– Putty for connecting to server
– A user with sudo privileges
– LAMP stack – If you haven’t installed LAMP stack on the server, follow our tutorial to install LAMP stack on Ubuntu 16.04.
Special Note: This tutorial will be installing next cloud on the sub domain name http://nextcloud.example1.com. Please don’t forget to change the example1 with your domain name. Check our virtual host file creation tutorial for adding a domain name to the web server.
It is a good habit to make sure that the system repositories are up to date before installing anything on the server. As usual, you can run the following command to update repositories
sudo apt-get update
Install NextCloud on Ubuntu 16.04
The complete installation and configuration of next cloud on Ubuntu server includes the following steps
- Installing PHP modules
- Download NextCloud to Server
- Installing NextCloud Files on Server
- Configuring Apache for NextCloud
- Create Database for NextCloud
- NextCloud Final Configuration
Installing PHP modules
We need to install additional modules than that installed during LAMP stack configuration to work NextCloud properly. To install required PHP modules, run the following command
sudo apt-get install php-gd php-json php-mysql php-curl php-intl php-mcrypt php-imagick php-zip php-dom php-xml php-mbstring
Please type Y when it asks for the confirmation to start the installation.
Download the latest version of NextCloud
In this step, we will fetch the latest release of NextCloud to our server using wget command. The latest version of the nextcloud can be found here
wget https://download.nextcloud.com/server/releases/latest-11.zip
This command will save the “latest-11.zip” file in the current directory
Use the “ls” command to list the file on current directory and confirm the file is fetched to the server.
Installing NextCloud on Server
In this step, we will extract the “latest-11.zip” file in the current directory using the following command.
unzip latest-11.zip
A new directory with the name nextcloud will be appeared upon extracting the zip file
We will move the nextcloud directory into the domain path. In my case, the domain name is “example1.com” and the domain path from the root is /var/www/example1.com/public_html
So I will use the following command in the putty box to move the nextcloud directory to the domain root path /var/www/example1.com/public_html
sudo mv nextcloud /var/www/example1.com/public_html
Now we have all the files required for nextcloud is in the correct directory. However, we need to fix the ownership issues and permissions for files and directories to work nextcloud properly.
You will receive an error message as like below when you try to access next cloud from the web browser before fixing the correct permission

We can fix all the permission and ownership issues of nextcloud by running an official shell script.
Create a new file named permissionfix.sh using the following command
sudo vi permissionfix.sh
Paste the following code into the permissionfix.sh. Please replace the “ocpath” with your actual path where your nextcloud files are placed
#!/bin/bash
ocpath=’/var/www/example1.com/public_html/nextcloud‘
htuser=’www-data’
htgroup=’www-data’
rootuser=’root’printf “Creating possible missing Directories\n”
mkdir -p $ocpath/data
mkdir -p $ocpath/updaterprintf “chmod Files and Directories\n”
find ${ocpath}/ -type f -print0 | xargs -0 chmod 0640
find ${ocpath}/ -type d -print0 | xargs -0 chmod 0750printf “chown Directories\n”
chown -R ${rootuser}:${htgroup} ${ocpath}/
chown -R ${htuser}:${htgroup} ${ocpath}/apps/
chown -R ${htuser}:${htgroup} ${ocpath}/config/
chown -R ${htuser}:${htgroup} ${ocpath}/data/
chown -R ${htuser}:${htgroup} ${ocpath}/themes/
chown -R ${htuser}:${htgroup} ${ocpath}/updater/chmod +x ${ocpath}/occ
printf “chmod/chown .htaccess\n”
if [ -f ${ocpath}/.htaccess ]
then
chmod 0644 ${ocpath}/.htaccess
chown ${rootuser}:${htgroup} ${ocpath}/.htaccess
fi
if [ -f ${ocpath}/data/.htaccess ]
then
chmod 0644 ${ocpath}/data/.htaccess
chown ${rootuser}:${htgroup} ${ocpath}/data/.htaccess
fi
Write and quit from the vi editor by pressing Esc:wq + Enter
Now run this script to fix the file permission issues by using the following command
sudo bash permissionfix.sh
Apache Configuration for NextCloud
To work nextcloud properly on the server, the mod_rewrite should be enabled on the server. Just release the following command to enable mod_rewrite on the apache server
sudo a2enmod rewrite
Please install the additional recommended modules by using the following command lines. If these modules are already present on the server, you will receive an already enabled message. Just ignore it and move ahead to next step
sudo a2enmod headers
sudo a2enmod env
sudo a2enmod dir
sudo a2enmod mime
Create apache configuration files by following the below steps
sudo vi /etc/apache2/sites-available/nextcloud.conf
Copy paste the following code into the file and save it. Please be vigilant to replace the paths in the following code with your actual path. Also add a “A” record on your domain root to access the subdomain
<VirtualHost *:80>
DocumentRoot “/var/www/example1.com/public_html/nextcloud”
ServerName nextcloud.example1.comErrorLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/error.log
CustomLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/access.log combined<Directory /var/www/example1.com/public_html/nextcloud/>
Options +FollowSymlinks
AllowOverride All<IfModule mod_dav.c>
Dav off
</IfModule>SetEnv HOME /var/www/example1.com/public_html/nextcloud
SetEnv HTTP_HOME /var/www/example1.com/public_html/nextcloud
Satisfy Any</Directory>
</VirtualHost>
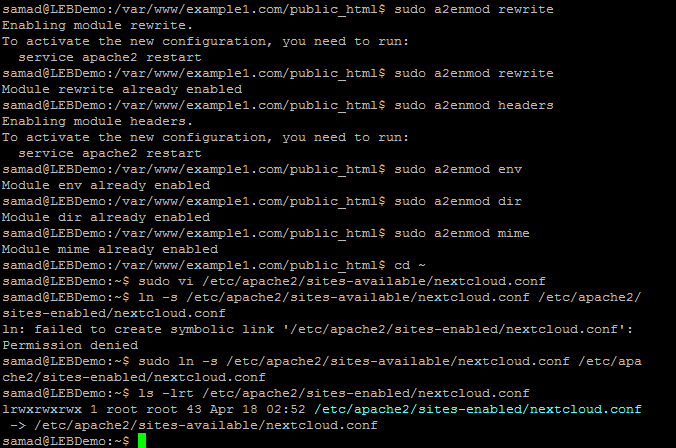
Now we need to create the symlink for this to /etc/apache2/sites-enabled
sudo a2ensite nextcloud
Even you can enable the site by using the following command
sudo ln -s /etc/apache2/sites-available/nextcloud.conf /etc/apache2/sites-enabled/nextcloud.conf
Once done, reload apache to activate the changes by releasing the following commands
sudo systemctl reload apache2
Create MySQL database for NextCloud
We have all the setup files ready for nextcloud installation. Now we need to create a database for nextcloud. Just follow the below procedure to create a database for the nextcloud.
Use the following command to access the MySQL database
mysql -u root -p
It will ask you to enter the MySQL root password. Please type your MySQL root password and enter to the MySQL command prompt
Now, create a database for nextcloud using the command below. You can replace the database name “ncdatabase” with any name that you wish. I suggest you not to use nextcloud as database name for security reasons.
CREATE DATABASE ncdatabase;
In the next step, we will create a database user and will assign the user to the created database with all privileges
CREATE USER ‘ncuser’@’localhost’ IDENTIFIED BY ‘MyStrongPassword@123’;
Replace “ncuser” with the database username you wish and “MyStrongPassword@123” with a strong password
Now assign the user “ncuser” to the database “ncdatabase” with all privileges. Please don’t forget to replace database user name and database name with your actual database name and username
GRANT ALL ON ncdatabase.* TO ‘ncuser’@’localhost’;
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
exit;
Next Cloud Final Configuration
In this step, we will configure the nextcloud through the web-based installation procedure. To start the installation, just load the domain name on a web browser.
In my case, I will load http://nextcloud.example1.com/ to initiate the installation
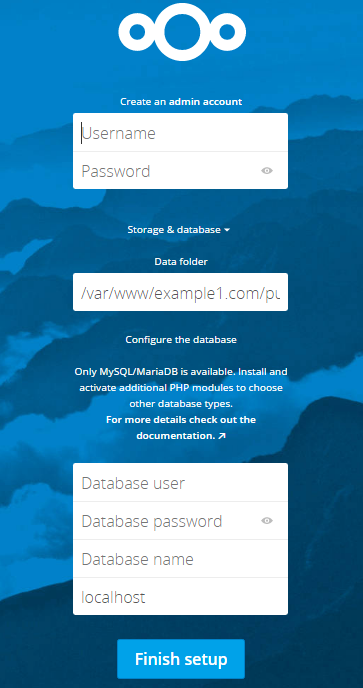
- Create an admin account by entering username and password. I suggest you to use an username other than admin and a strong password
- Data folder will be fetched by the script automatically. Verify that it is correct
- You have to enter the database details correctly
- In my case, the database user is “ncuser”, database password is “MyStrongPassword@123” and Database name is “ncdatabase”.
- Database hostname will be filled by default as localhost
- Click on “Finish Setup” after filling out all the details correctly to finish the installation

After the successful installation, you will receive the following screen on your browser where you can start managing your files
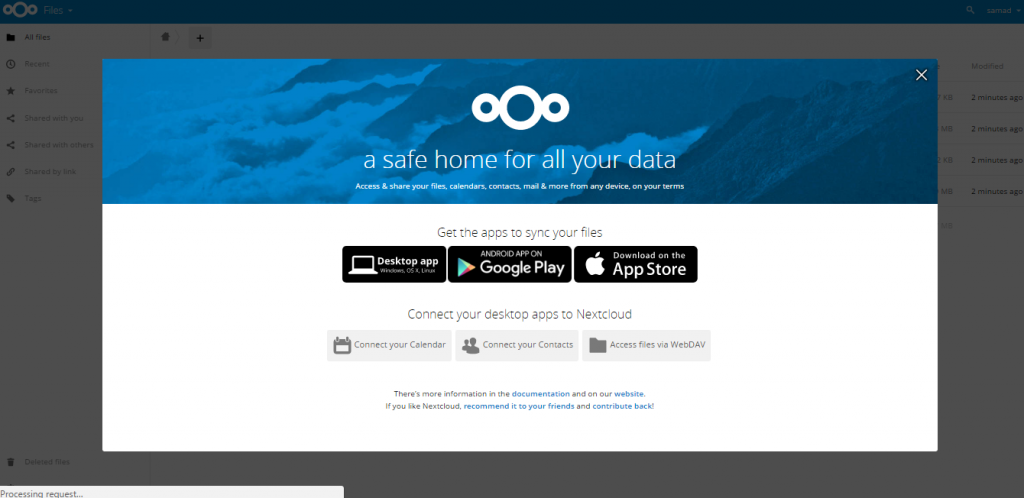
Conclusion
If you have followed our tutorial correctly, you will be on the nextcloud dashboard right now. Just refer the official administration manual to configure additional settings for nextcloud.
Let us know if you face any issue with nextcloud installation on Ubuntu 16.04



















That’s possibly the nicest nextcloud walkthrough I’ve seen. To make it even better, it would be great to add a SSL workflow, i.e. how to setup with LetsEncrypt.
Thanks for the feedback! We’ll see what we can do!
Yep..SSL workflow would be great! Thanks!
You should update the tutorial to take into consideration the hardening recommendations from nextcloud. Simple things like keeping the “data” folder outside of the web root given you have put together scripts to handle this sort of things.
Also, SSL is cheap and easy, I agree with the other posters. Just getting it up and running is not really useful given the constant attacks/bots/scanning.
You’re doing a disservice to your readers by not taking into account the basics of security and safe hosting.